Types of Common and Dangerous Poisons
If you are or someone else is exposed to any poisonous product or substance, use the webPOISONCONTROL® tool to get specific first aid and treatment recommendations online. You can also call 1-800-222-1222. Both options are free, confidential, available 24/7, and provide expert help.
What are the most common types of poison exposures in children?
Did you know that even these common household items can poison children?
- cosmetics and personal care products
- cleaning substances and laundry products
- pain medications, both prescription and over-the-counter (OTC)
- foreign bodies such as toys and toy parts, coins, and thermometers
- topical preparations like rash creams
- vitamins and supplements
- antihistamines
- pesticides
- plants
- antimicrobials like antibiotics
Pediatric Poisonings Data
- To see data on the most common types of pediatric poisonings managed by webPOISONCONTROL, visit the interactive data dashboard's "Top 10 and Top 10 for Kids (<6 years)."
- To see data on the most common types of pediatric poisonings reported by Poison Control callers, click here.
What are the most common types of poison exposures in adults?
- pain medicines, both prescription and over-the-counter (OTC)
- sedatives, hypnotics, antipsychotics
- antidepressants (SSRIs and SNRIs)
- cardiovascular drugs
- cleaning substances (household)
- alcohols
- pesticides
- bites and envenomations (ticks, spiders, bees, snakes)
- anticonvulsants
- cosmetics and personal care products
Adult Poisonings Data
- To see data on the most common types of adult poisonings managed by webPOISONCONTROL, visit the interactive data dashboard's "Top 10 and Top 10 for Kids (<6 years)."
- To see data on the most common types of adult poisonings reported by Poison Control callers, click here.
What are the most dangerous types of poisons for children?
- Medications: Medicines are OK in the right amount for the right person, but they can be dangerous for children who take the wrong medicine or ingest too much. And we don't just mean prescription medications; even some over-the-counter medicines can be very dangerous!
- Carbon monoxide: Not all poisons are swallowed; some are inhaled, or breathed in. Carbon monoxide gas is in fact an invisible killer. It has no color or odor. Take it seriously. Make sure there's a carbon monoxide alarm in every sleeping area of your home.
- Button batteries: Button batteries (sometimes called disc batteries) can be found in musical greeting cards, remote controls, key fobs, and other small electronic devices. Be especially mindful of the 20 mm lithium coin cell battery. When swallowed by a child, especially one younger than 4 years, it often lodges in the esophagus causing burns within just 2 hours. A hole in the esophagus may develop and the burn can extend into the trachea or aorta. More than 60 children have died from ingesting button batteries.
- Iron pills: Adult-strength iron pills are very dangerous for children to ingest. Children can start throwing up blood or having bloody diarrhea in less than an hour.
- Cleaning products that cause chemical burns: These can be just as bad as burns from fire. Products that cause chemical burns include drain openers, toilet bowl cleaners, rust removers, and oven cleaners. Inhalation of bleach, toilet bowl cleaner, the contents of laundry detergent pods, oven and drain cleaners are also poison hazards.
- Nail glue remover and nail primer: Some products used for artificial nails can be poisonous in surprising ways. Some nail glue removers have caused cyanide poisoning when ingested by children. Some nail primers have caused burns to the skin and mouth of children who tried to drink them.
- Hydrocarbons: This is a broad category that includes gasoline, kerosene, lamp oil, motor oil, lighter fluid, furniture polish, and paint thinner. These liquids are easy to choke on if someone tries to swallow them. If that happens, they can go down into the lungs instead of the stomach. If a hydrocarbon gets into someone’s lungs, it can make it hard to breathe. They can also cause lung inflammation (like pneumonia). Hydrocarbons are among the leading causes of poisoning death in children.
- Pesticides: Chemicals to kill bugs and other pests must be used carefully to keep from harming humans. Many pesticides can be absorbed through skin. Many can also enter the body by inhaling the fumes. Some can affect the nervous system and can make it hard to breathe.
- Windshield washer solution and antifreeze: Small amounts of these liquids are poisonous to humans and pets. Windshield washer solution can cause blindness and death if swallowed. Antifreeze can cause kidney failure and death if swallowed.
- Wild mushrooms: Many types of mushrooms grow in many areas of the country. Some are deadly to eat. Only experts in mushroom identification can tell the difference between poisonous mushrooms and safe mushrooms.
- Alcohol: When children swallow alcohol, they can have seizures, go into a coma, or even die. This is true no matter where the alcohol comes from. Mouthwash, facial cleaners, and hair tonics can have as much alcohol in them as alcoholic beverages.
- Drain cleaners and toilet bowl cleaners: These caustics cause devastating burns to the mouth, throat and stomach. Drain cleaners may be strongly alkaline and toilet bowl cleaners may be strong acids. If swallowed, they must be diluted immediately to limit the damage that rapidly occurs.
- Topical anesthetics: These medicines can cause seizures or a condition called methemoglobinemia which keeps the blood from carrying oxygen to the tissues. Be especially careful with teething gels, hemorrhoid preparations, anti-itch creams, and sunburn relief agents.
Food Poisoning
Did you know that there are more than 250 types of food poisoning? Food poisoning can happen to anyone, regardless of age. To learn more about food poisoning, its causes, and how to prevent it, visit our Food Poisoning page.
Top Poisoning Prevention Tips
You can help prevent poisonings by:
1. Being prepared for an emergency and acting fast if you suspect a poisoning, even if you aren’t sure.
- Save the national Poison Control number in your phone and post it in your home. 1-800-222-1222. It’s free, private, and calls are answered by experts. Those experts have heard it all. Don’t be embarrassed to call.
- Don’t want to use the phone? Bookmark www.poison.org or download the webPOISONCONTROL app on the App Store or Google Play. Poison Control guidance is available online for those who can’t or prefer not to call.
2. Practicing safe storage habits.
- Certain substances like those listed above can be particularly dangerous for kids. Those items should be stored up, away, and out of sight. For things that can’t be stored safely, use child-resistant cabinets and containers. But keep in mind that there is no such thing as a “child-proof" container!
- Keep products in their original containers. Don’t put non-food or non-beverage substances in containers meant for consumables.
3. Reading and following labels and directions.
- Review product labels prior to their use, especially before taking or administering medications.
- Follow usage instructions as well as those about safe storage and disposal.
4. Preventing danger from invisible threats.
- Install carbon monoxide detectors in your home.
- Install radon detectors if your home is at risk.
Click here to order free poisoning prevention materials from your local Poison Center for your home, workplace, school, or to distribute at events.
If you are or someone else is exposed to any poisonous product or substance, use the webPOISONCONTROL® tool to get specific first aid and treatment recommendations online. You can also call 1-800-222-1222. Both options are free, confidential, available 24/7, and provide expert help.
Poisoned? Get Expert Help.
Don't guess what you should do. Get accurate Poison Control answers online or by phone. Both are free and confidential.
or CALL 1-800-222-1222
Connect with us
on social media!
Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter for news, updates, and events!
Add Poison Control to your phone’s contacts
You're invited!

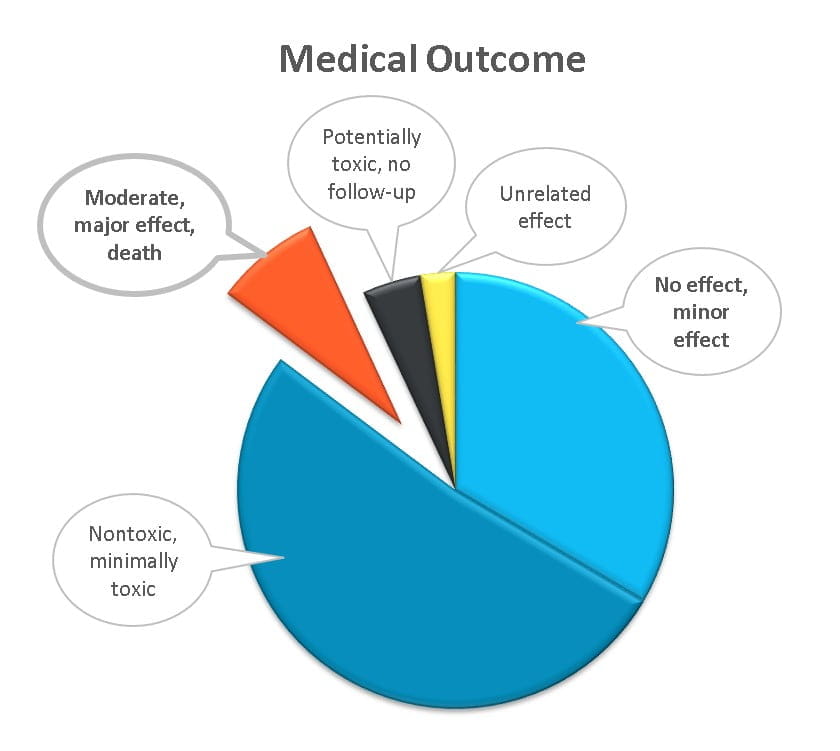
Poison Statistics
Support Us
Your donation to our 501(c)(3) organization enables us to help those who prefer to go online when faced with a poison emergency. Our webPOISONCONTROL online tool and app is a free, confidential, quick and easy way to get expert help. It has guided more than a million users faced with a poison emergency.