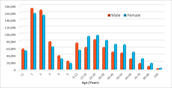
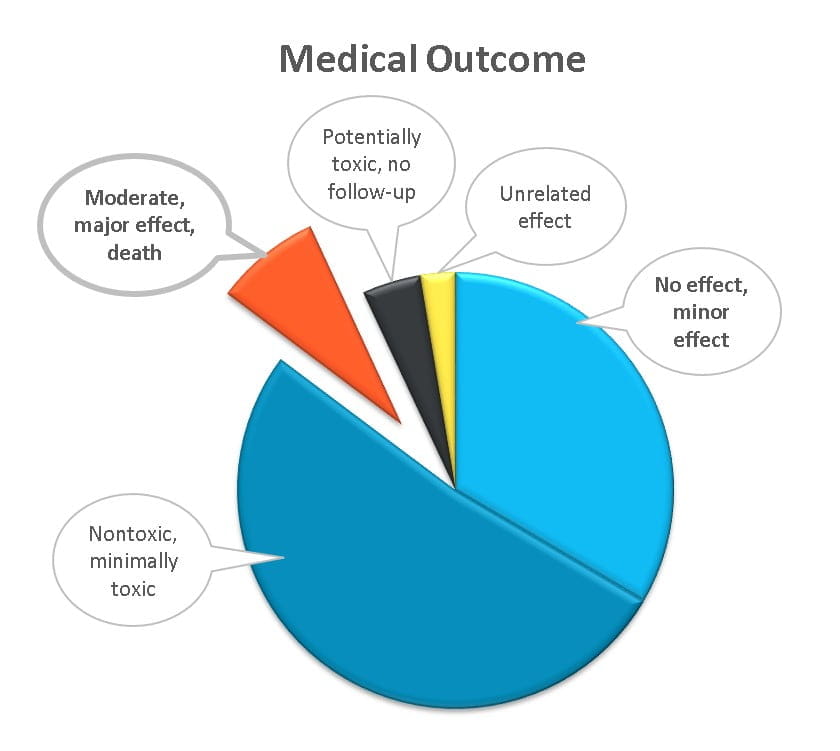
Benefits and Side Effects of Indapamide
Indapamide is a medication for high blood pressure that appears to be better than many other drugs at controlling high blood pressure while lowering the risk of heart failure. However, indapamide can sometimes cause patients to become dehydrated and lose potassium. Adverse effects can last for several days after the drug is taken.