What is Xylazine?
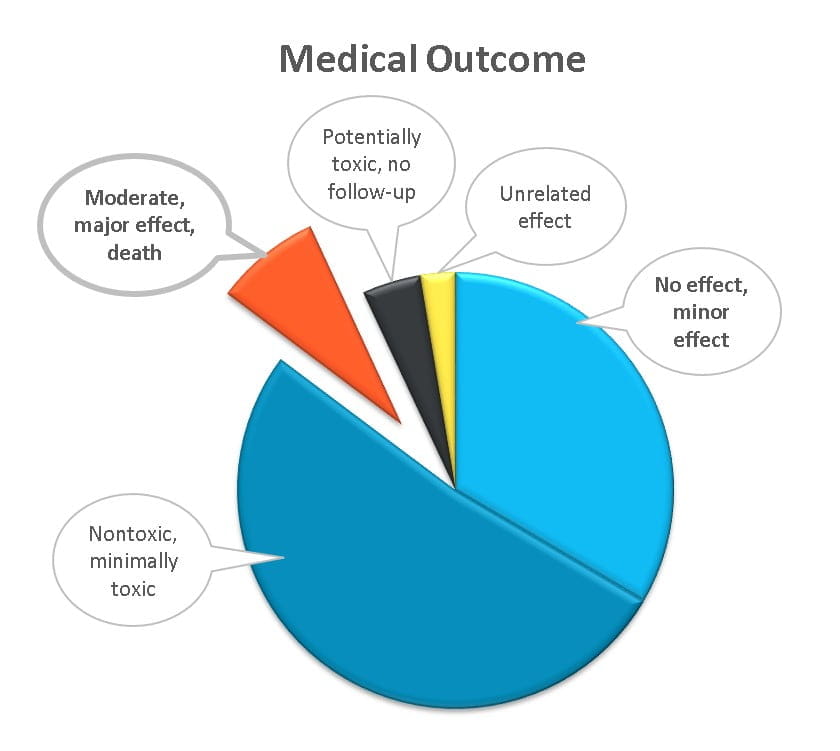
Xylazine, also known as "tranq," is a powerful animal tranquilizer. Although it is not intended for human use, xylazine is a common contaminant of illicit drugs in the U.S. It can worsen toxic effects of some drugs. Xylazine use causes sleepiness and a slow respiratory rate and might result in development of necrotic skin wounds (skin wounds with dead tissue).